DNA Database and Parentage Testing Section
DNA Database and Parentage Testing Section comprises DNA Database Unit and Parentage Testing Unit.
DNA Database Unit
An Amendment Bill to three of the security-related ordinances, namely the Dangerous Drugs, Independent Commission Against Corruption and Police Force (Amendment) Bill 2000 was introduced to the Legislative Council in the beginning of the year 2000. After some twenty meetings in which members of the Council deliberated in detail its contents, the Bill was finally passed as Ordinance in June 2000. In the Dangerous Drugs, Independent Commission Against Corruption and Police Force (Amendment) Ordinance 2000, provisions were made for the setting up and maintaining by the Government Laboratory, on behalf of the Commissioner of Police, a database storing DNA information of persons convicted of a serious arrestable offence.
The main responsibilities of this Unit are to perform DNA analysis on samples from persons convicted of a serious arrestable offence, those suspected of having committed a criminal offence and volunteers, set up in computerized form a DNA database and administer and maintain that database.
A DNA database on convicted persons is only useful for crime investigation if the information could be compared against DNA information of unsolved cases. Whilst DNA information of unsolved cases will be generated by the Biochemical Sciences Sections, both the DNA Database Unit and the Biochemical Sciences Sections will have to use the same techniques for information to be compatible and comparable.
Key Instruments
The following instruments are used routinely by the Unit:
- Liquid handling robotic system
- Genetic analyzer
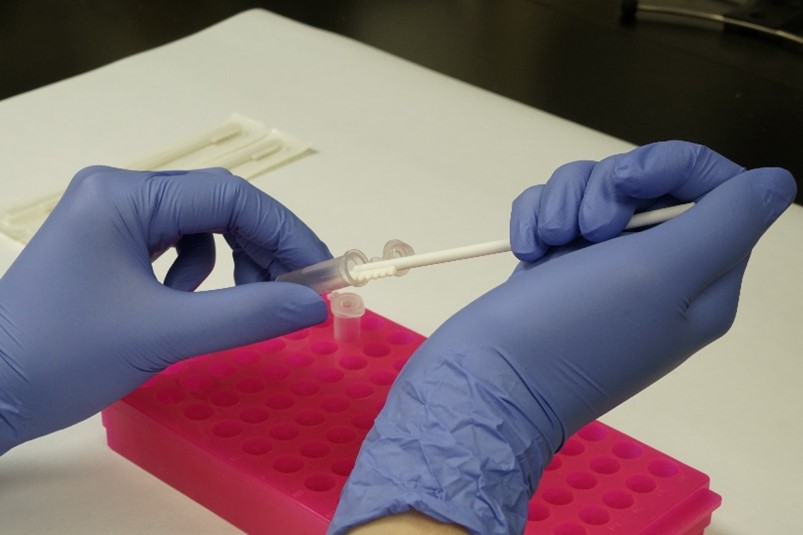
Preparation for extracting DNA from buccal swab
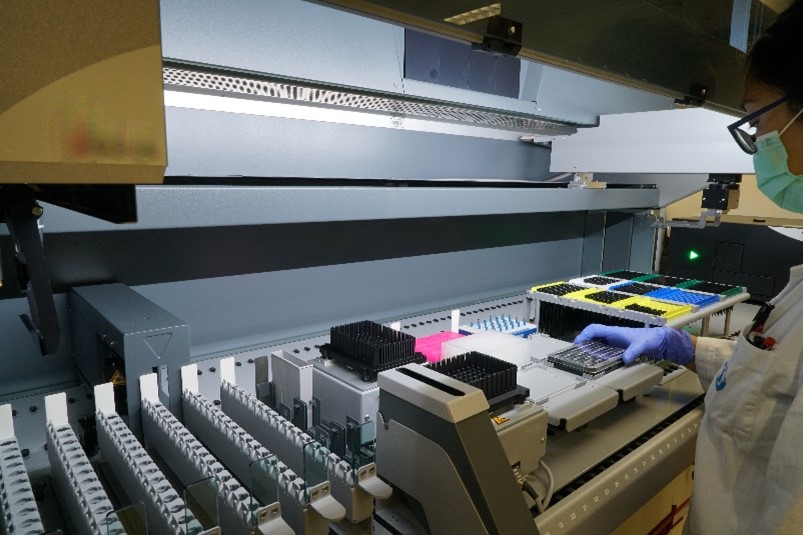

Robotic Liquid Handling System in operation
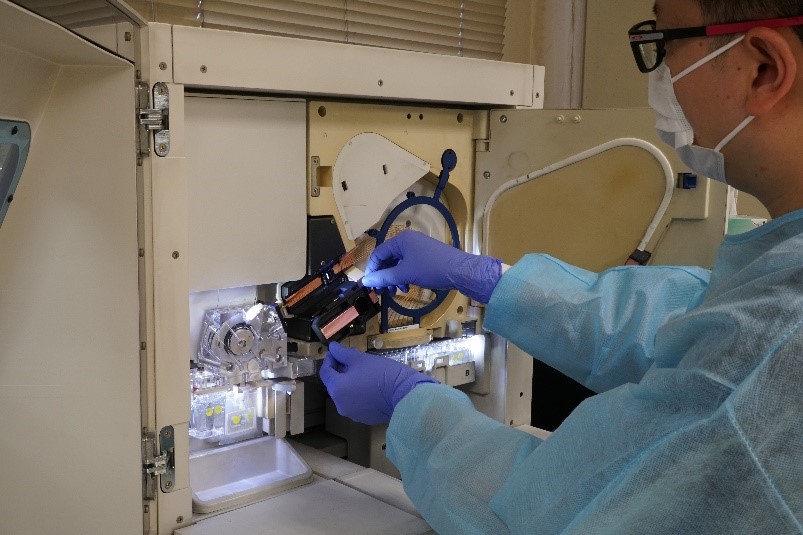

Conducting DNA testing by Genetic Analyzer
Targets and Key Indicators
Key Performance Measures Relating to the Forensic Science Services
Targets
Targets are defined as the percentage of completed cases whose individual case-completion time does not exceed a specified number of working day(s).
Key Indicators
Parentage Testing Unit
Parentage Testing Unit is employing DNA testing technique to verify the parent/child relationships in connection with immigration-related cases.
This Unit mainly provides service to persons who claim Right of Abode (ROA) under paragraph 2(c) of Schedule 1 to the Immigration Ordinance. Persons claiming ROA under the provision have to apply for a Certificate of Entitlement (C of E) in such manner as prescribed by the Director of Immigration by notice in Gazette pursuant to section 2AB(2) of the Immigration Ordinance. This Ordinance has been amended to empower the Director of Immigration in the assessment of an C of E application where he is not otherwise satisfied with the claimed parent and child relation on the basis of proof submitted by or on behalf of an applicant to request the application and the claimed parent(s) to undergo a specified genetic test. Pursuant to the Immigration (Amendment) Ordinance 2001, the Director of Immigration, by notice dated 27 July 2001 published in the Gazette, specified a genetic test procedure and designated the Hong Kong Government Laboratory as being responsible for carrying out such tests in Hong Kong. For related information, please check the homepage of the Immigration Department (http://www.immd.gov.hk).
Besides C of E applications, other immigration-related parentage claims may also be submitted to this Unit for verification.
The Parentage Testing Unit applies Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - based analysis of Short Tandem Repeats (STR) of DNA fragments for the verification of parent/child relationships. For the sensitivity of the PCR technique, epithelial cells collected through the swabbing of the inside of the cheeks of a person provide enough DNA and are used as the sample for analysis.
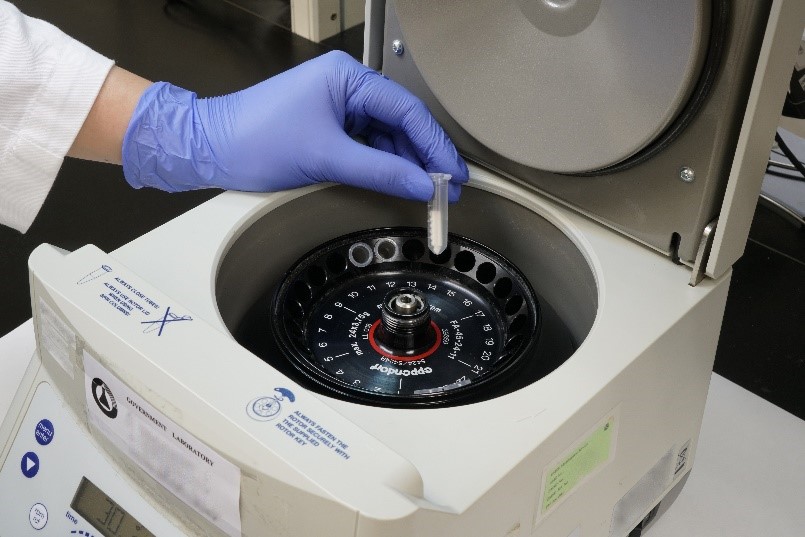
The extraction of human DNA from buccal swabs with the aid of a centrifuge
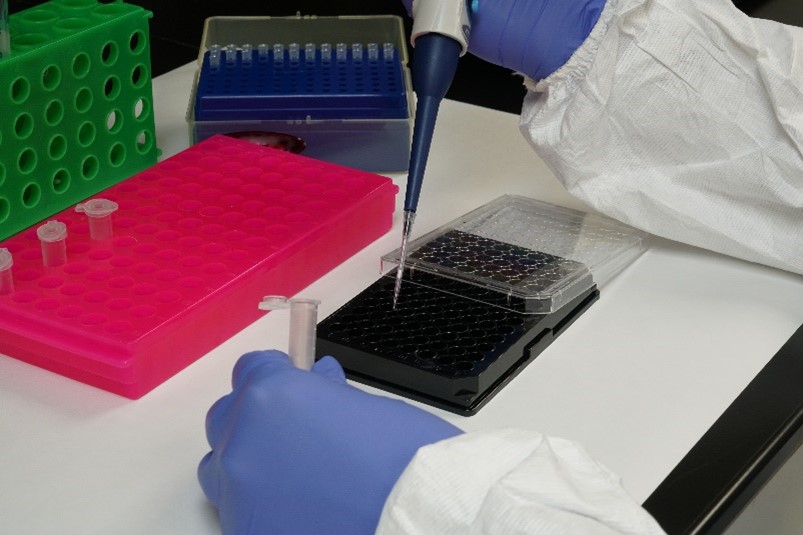

The estimation of DNA concentration in the buccal swab extract prior to the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
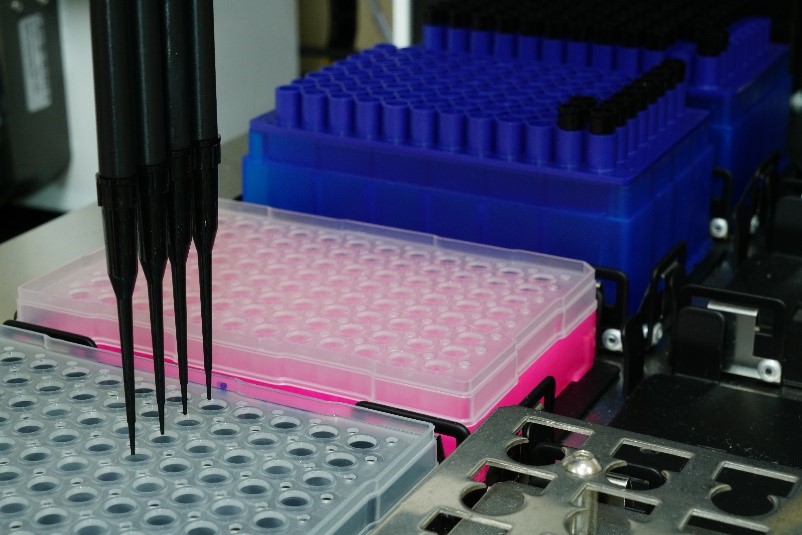

Employing a Robotic Liquid Handling System to process large volume of samples efficiently
Key Instruments
The following instruments are used routinely by the Unit:
- Photometric microplate reader
- Thermal cycler PCR amplification system
- Genetic analyzer
Targets and Key Indicators
Key Performance Measures Relating to the Forensic Science Services
Targets
Targets are defined as the percentage of completed cases whose individual case-completion time does not exceed a specified number of working day(s).
Δ The figures represent the number of working days lapsed between the reception by the Laboratory of samples for genetic testing and the issuing of genetic data after completion of DNA analysis of these samples within the Laboratory.
